Discovering Your Dog's Age in Human Years
Discovering Your Dog's Age in Human Years
Blog Article
Knowledge your dog's era in human decades is more than just a passing curiosity. It includes understanding in to your pet's living point, supporting you cater with their wellness, diet, and activity needs more effectively. But while the widely-known How to figure out dog years to human years formula is popular, it doesn't completely reveal reality.
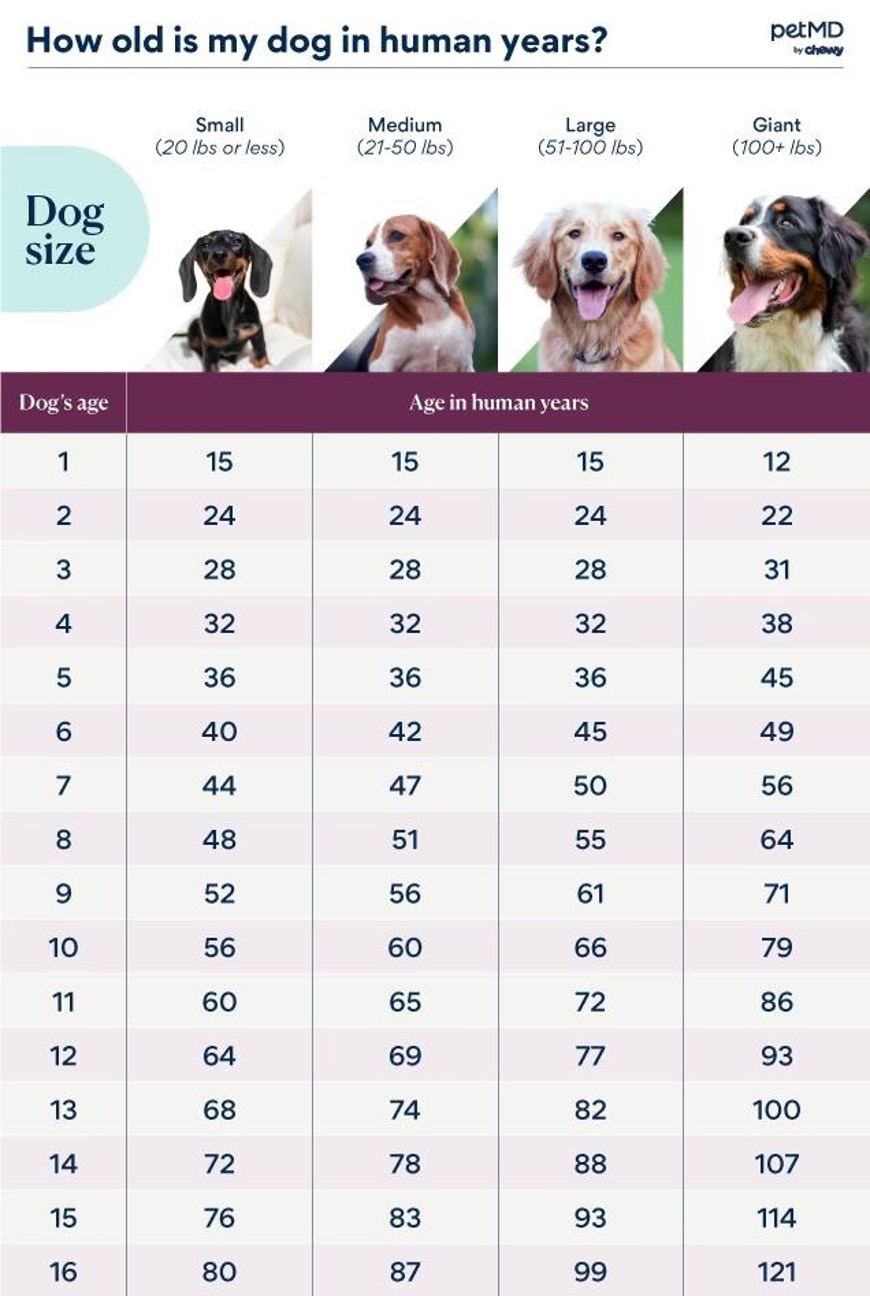
The Technology Behind Pet Decades
The 7-to-1 concept oversimplifies how pets age. The speed of aging varies based on a dog's measurement, type, and their early development. Smaller breeds often era slower and live lengthier, while greater breeds era easily and normally have faster lifespans.
Scientists at the College of Colorado produced a study centered on a dog's epigenetic clock (how DNA changes over time) to calculate ageing more accurately. According for their conclusions, a 1-year-old dog is approximately equivalent to a 30-year-old human because of quick development in the early years. By the full time canine is 2 years of age, their individual age is approximately 42. Following this point, the ageing method slows significantly.
A Breed-Specific Dysfunction
Here's a normal perception on ageing across breeds:
Little Breeds (e.g., Dachshunds, Chihuahuas)
These pets era gradually, and by their first year, they might be akin to a 15-year-old human. By the second year, they're roughly 24 in human years. Each subsequent year gives 4-5 human years.
Moderate Breeds (e.g., Bulldogs, Beagles)
Medium-sized pets follow a somewhat faster trajectory than smaller dogs. By age 2, they may be about 28 human years old, with each following year equating to 5-6 human years.
Big Breeds (e.g., Labrador Retrievers, Shepherds)
Larger breeds show noticeable accelerated aging. A 1-year-old big dog's development correlates to a 15-year-old human, advancing to 49 individual decades by age 5.
Tailoring Care to Their "Human Age"
By calculating your dog's human-equivalent age, you'll obtain a better knowledge of how to manage their living stage. As an example:
Puppies (human baby equivalent): Concentrate on training and socialization.
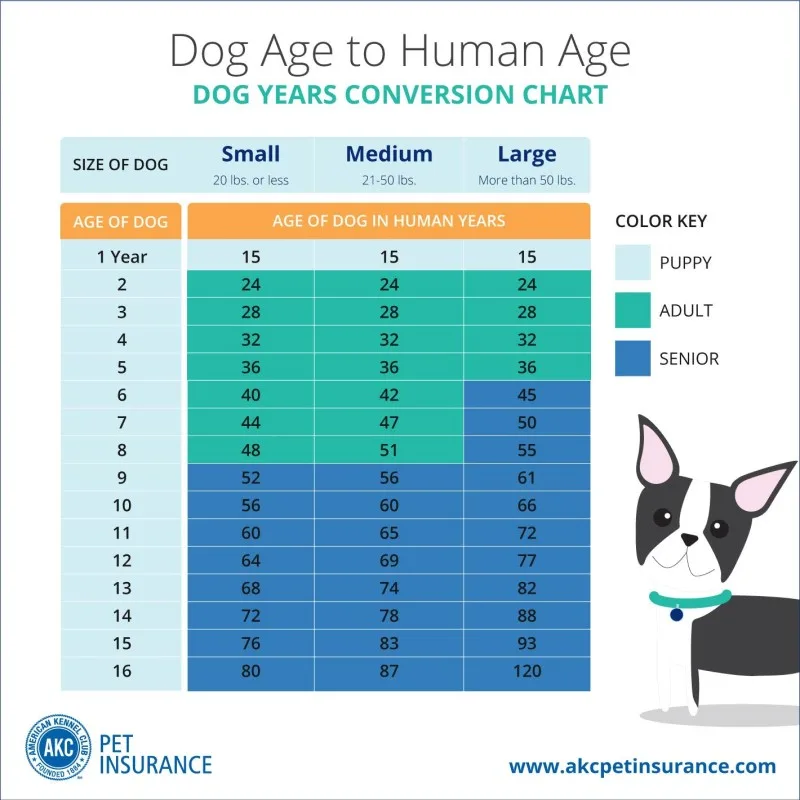
Person pets (human late 20s to 50s equivalent): Maintain their energy with a balanced diet and standard exercise.
Senior pets (human 60+ equivalent): Spend particular attention to joint health, standard veterinarian trips, and smoother diets.
The relationship of pet decades to human decades allows puppy homeowners the data they need to ensure their fuzzy buddies live the happiest and healthiest lives possible.
Report this page